Knowledge is “awareness or familiarity gained by experience of a fact or situation”.
A module is a “standardized, often interchangeable component of a system designed for easy assembly and flexible use.
CoreTech’s Knowledge Modules are comprised of hardware systems, software programs, and personal insights that can be integrated into the operation of any nonprofit or social enterprise.
Part of using Knowledge Modules includes an assessment which, using various rubrics, measures performance baselines. With these initial assessments, the effect of modified hardware, software, and other policies can be better assessed for further iterative changes.
Simply put: CoreTech, through the use of Knowledge Modules, is able to take a big picture view of an enterprise. With that picture, they are able to create SMART Goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-based.) These measurements shape the goals and enable CoreTech to monitor progress and improvement as they assist an enterprise with the adoption of cohesive software and hardware upgrades.
A great example of this is LiQuid, one of The Coretech Foundation’s flagship initiatives.
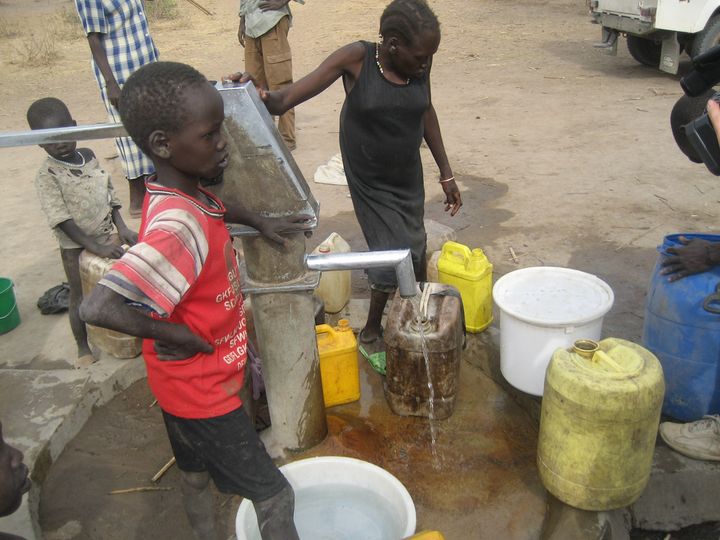
Using Knowledge Modules, CoreTech was able to access many factors which hinder the work of NGO’s working to provide clean water to developing countries. Through their assessment, CoreTech was able to discern some of the primary obstacles which degraded performance of enterprises that were designed to get people clean water.
Obstacles included: transaction fees; coordination of governments, NGOs, resources, and users; unstable currencies and economies. To address these hindrances, LiQuid created an alternative to money (water tokens) using a blockchain ledger, similar to what empowers BitCoin. This eliminated the funds lost to transaction fees. LiQuid created a system which allowed NGOs and Governments to consolidate themselves and their resources, reducing redundancies and gaps. Lastly, LiQuid addressed the complications of unstable currencies and economies with the water token which now stimulates social entrepreneurship and ensures consistent exchange despite regional economic fluctuations.
This is one example of CoreTech’s Knowledge Modules put into action. The assessment of a situation which enables the application of IT which reduces person hours, cuts costs, improves efficiency, and improves accountability.
Read this for more examples of Nonprofits which have leveraged the power of Technology to improve their positive effect.
photo credit: Water for South Sudan, Inc.