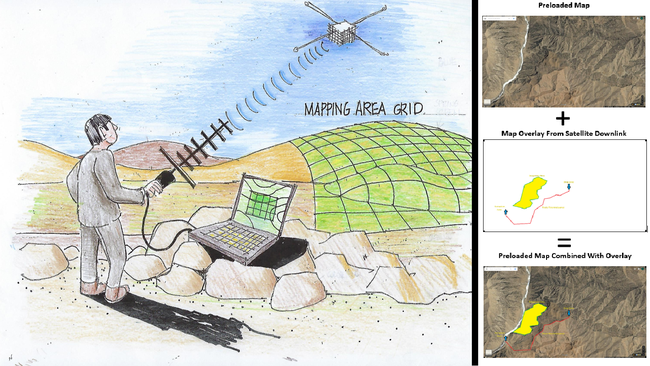
All required software is open source.
No specialized GIS software needs to be created.
This can be accomplished using existing technology.
Software:
• GIF or PNG Images
• ImageMagick
• HTML and CSS
• Any image editor such as Paint, GIMP, Photoshop, etc..
Hardware:
• Raspberry Pi 3 Model B (satellite)
• Micro SD card 128 GB (satellite)
• Military-grade, rugged notebook (ground station)
• Handheld transceiver (ground station)
• Collapsible Yagi antenna (ground station)
Software Setup:
• This can be accomplished using GIF or PNG image files with transparency.
• Existing open-source software called ImageMagick can easily separate the annotations from the map. In fact, I have already included working code in the attachment.
• CSS and HTML language which is already included with every browser can join the annotations with the maps. I have also included working code for this in the attachment.
• Development of complex GIS software is unnecessary.
• Onboard Satellite Prioritization algorithm will determine what to upload or download based on priority and limited time.
Hardware Suitability:
Typical Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites can be expected to receive a Total Ionizing Dose (TID) of 1.2 krad(Si).
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/6cbd/40e77f381775a37e6dbed10edc5e13ace1a0.pdfRaspberry Pi Model B boards have been tested to handle up to 40 krad(Si).
https://nepp.nasa.gov/workshops/eeesmallmissions/talks/11%20-%20THUR/1430%20-%202014-561-%20Violette-Final-Pres-EEE-TN17486%20v2.pdfMicroSD memory cards have been tested to handle up to 8 krad(Si).
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/6cbd/40e77f381775a37e6dbed10edc5e13ace1a0.pdf